
A small amount of radioactive material is injected around the cancer or under the nipple. It is usually performed in a nuclear medicine or X-ray department. Lymphatic mapping is performed the day before, or a few hours before surgery. These techniques produce a ‘road map’ to help the surgeon find the sentinel node for removal during the operation.
lymphoedema (permanent swelling of the arm due to a build-up of fluid in the tissues) - see the ‘ Lymphoedema’ Fact Sheet for more information.seroma (a collection of fluid under the arm in the weeks after surgery).numbness of the inner aspect of the upper arm.Because all of the lymph nodes are removed, axillary clearance also helps to reduce the chance of the breast cancer coming back in the armpit in the future.Īxillary clearance has some possible side effects. Axillary clearance is a very effective operation to get information about whether or not the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. This operation is called axillary clearance or axillary dissection.

In the past, the usual operation for breast cancer was to remove most, if not all of the lymph nodes from the armpit on the same side as the breast cancer. Smaller breast cancers are less likely to involve the lymph nodes. The chance of cancer spreading to the lymph nodes is partly determined by the size of the cancer.
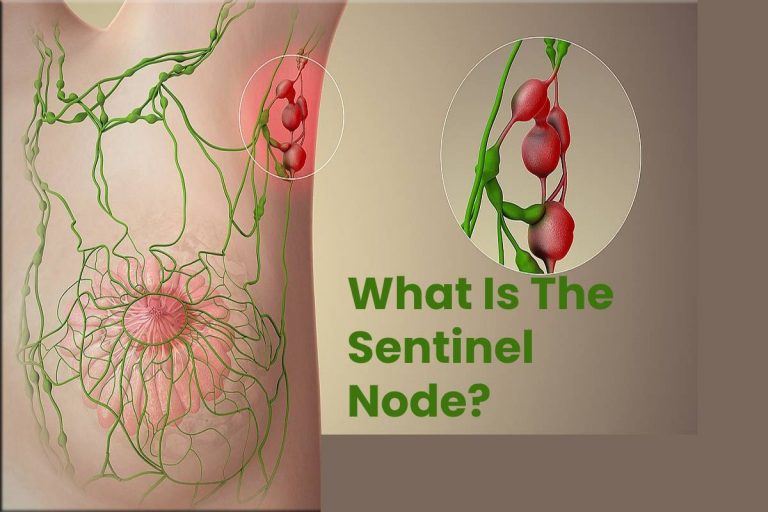
Overall, about 70% of women with breast cancer will not have cancer in the lymph glands. Testing the lymph nodes is very important, as it gives you and your doctor information about the breast cancer. Treatment for breast cancer usually involves removing some lymph nodes as well as removing the cancer from the breast. Other lymph nodes that can become involved with breast cancer are located near the collarbone and behind the breastbone. The lymph nodes that filter waste fluid and cells from the breast are mainly located in the armpit (also called the axilla.) These lymph nodes are usually the first ones affected if cancer spreads beyond the breast. Tiny channels (called lymphatics) carry fluid and debris to the lymph nodes which act as filters. Lymph nodes (also called lymph glands) are part of the body’s immune system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
